Plate and frame heat transfer is a proven technology that has been around for many decades and continues to be relevant in the heat transfer market and across multiple industries
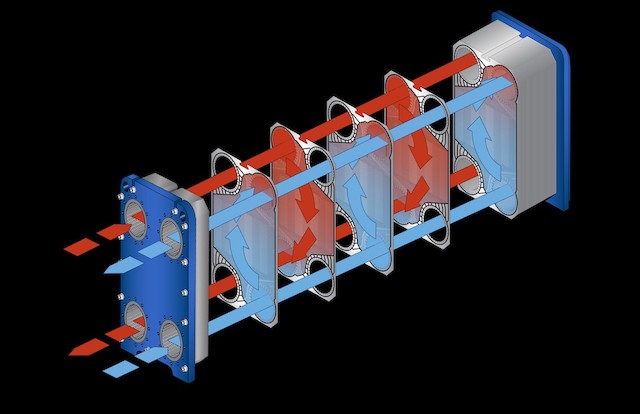
Plate and frame heat exchangers insights
- Plate and frame heat exchangers provide a high level of thermal efficiency, resulting in improved performance and cost savings.
- The flexibility in their design makes plate and frame heat exchangers an effective and efficient solution for a variety of applications.
- The design of plate and frame heat exchangers simplifies maintenance, lowering costs and risk of potential downtime.
Gasketed plate and frame heat exchangers have been and continue to be an integral part of the heat transfer industry. Their use spans multiple industries and applications where liquid to liquid heat transfer is present. The gasketed plate and frame technology was originally developed in the 1920s and has revolutionized thermal management by providing exceptional heat transfer efficiency and ease of maintenance compared to other types of heat transfer not rooted on plate type technology (such as shell and tube). Their proven effectiveness has made them a go-to thermal technology for many applications in heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems.
Structured for efficiency
Plate and frame heat exchangers stand out for their high thermal efficiency, making them useful in a variety of heat transfer applications. At the core of their efficiency is the unique design that employs a series of thin, corrugated plates (see Figure 1). These plates are arranged in a frame, creating multiple channels for fluids to flow through. These channels measure in mere millimeters, allowing many plates to be stacked side by side. This arrangement maximizes the surface area for heat transfer while maintaining a compact footprint, enabling efficient thermal exchange between the fluids.
Corrugated plates induce turbulence even at low-flow velocities, significantly enhancing the heat transfer coefficient. As a result, the increased turbulence reduces the potential for fouling, which allows for extended maintenance-free operation.
Another aspect of their efficiency is their compact size, which minimizes the amount of material required for construction. This lowers the initial investment and makes plate and frame heat exchangers a cost-effective solution for various applications. Furthermore, the compact design contributes to lower fluid holdup requirement within the system (glycol usage, for example), enhancing their environmental benefit. In the case of the semi-welded design, used in refrigeration applications, less ammonia charge is required than in a traditional refrigeration system.

Key applications of plate and frame heat exchangers
One key application where plate and frame heat exchangers provide a big impact is free cooling. It is an environmentally friendly way to produce chilled water without the use of electricity-intensive or refrigerant-based mechanical cooling. Wide use of free cooling can be found in air conditioning and other process cooling applications. It is implemented when the cooling source is at a lower temperature than the desired temperature of the process cooling media (typically during spring, fall and winter seasons). Air is a widely used cooling source; however, ground water, rivers and lakes can serve as an alternate source.
Heat recovery is another application where this technology plays a big role. As the reduction in carbon footprint continues to be the primary goal for the foreseeable future, heat exchangers are an integral part in this effort. Recovering heat from any process where it would otherwise be discarded into the surrounding environment allows us to tap into a resource, which provides significant energy savings and reduction of emissions.
Future-proof through flexibility
The flexibility of plate and frame heat exchangers caters to the dynamic needs of various industries. Because the corrugated plates are pressed from a thin continuous coil, they can be arranged into various sizes. Taller/longer plates allow for longer bed time with the heat transfer fluid, which enables the plates to excel in heat transfer applications where a large temperature drop is desired. Shorter plates cater to applications with height and pressure drop limitations and can be arranged in a multipass configuration allowing for a longer bed time.
As a result, plate and frame heat exchangers can achieve high thermal performance with relatively small temperature differences between the hot and cold fluids, reducing energy consumption and operational costs.
Furthermore, their modular nature and versatile plate design allows for easy customization and scalability across various applications. To meet operational needs, these heat exchangers can be equipped with various plate designs (see Table 1). Additional plates can be added to the existing setup to increase capacity or to accommodate changes in process requirements. This adaptability ensures that the heat exchanger can grow with the process needs, providing a future-proof solution.

Plate and frame heat exchangers can be constructed from a wide range of materials, including stainless steel, titanium and various other alloys, to handle different types of fluids and operating conditions. This versatility makes them suitable for applications across sectors such as HVAC, food, beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, chemical manufacturing and power generation.
Maintenance in plate and frame heat exchangers
Ease of maintenance is another benefit of plate and frame heat exchangers. Unlike shell-and-tube heat exchangers, which can be cumbersome and time-consuming to service, plate and frame heat exchangers are designed for straightforward maintenance. The plates can be easily accessed by loosening the bolts on the frame and sliding the plates apart.
This accessibility allows for quick inspection, cleaning and replacement of individual plates if necessary. The gasketed design further simplifies maintenance, as gaskets can be replaced without any glue or the need for any specialized tools. The heat exchanger can be cleaned without any disassembly using a backflush valve.
The durability and longevity of plate and frame heat exchangers further highlight their value. The materials and various plate designs used in their construction are carefully chosen by the design team for their resistance to corrosion, fouling and wear to ensure that the heat exchangers can withstand harsh operating conditions over extended periods of time. This durability reduces the frequency and cost of replacements, contributing to long-term operational savings. Moreover, the efficient design and ease of maintenance mean that plate and frame heat exchangers can maintain their performance over time, providing consistent and reliable service to the owner.
Plate and frame heat exchangers offer a blend of efficiency, flexibility and ease of maintenance that makes them a desirable choice for a wide range of HVAC and industrial applications. Their unique design maximizes heat transfer while minimizing space and material requirements, leading to cost-effective and energy-efficient operations. The modular and versatile nature of these heat exchangers allows them to adapt to changing process demands, providing long-term flexibility and scalability. Their thermal efficiency, ease of maintenance and durable construction ensure that they remain a reliable and durable component of various heating and cooling processes, contributing to enhanced operational efficiency and productivity.




