Jason Gerke discusses ASHRAE 135, also known as BACnet, that is a standard that enables interoperability and data exchange in building control systems.
Learning Objectives
- Gain a basic understanding of ASHRAE 135: BACnet — A Data Communication Protocol for Building Automation and Control Networks.
- Understand building automation systems and how they can improve building efficiency.
- Additional audience questions are answered.
BACnet insights
- BACnet allows for the transfer of encoded data between devices, enabling the exchange of various types of information such as hardware values, schedules, alarms and trend data.
- Control systems enhance building operation and efficiency by creating a centralized method for operating various building systems such as HVAC, lighting, shading and security.
This is a partial transcript from a March 2023 webcast, “HVAC and BAS: Can BACnet control an HVAC system?,” available Jason Gerke, PE, LEED AP VD+C, CxA, principal, GRAEF, discusses how BACnet enables interoperability and data exchange in building control systems.
What is ASHRAE 135?
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) created the It has roots to the mid-1990s when it was issued as a continuous maintenance standard. The standard became ANSI-approved in 2001 and the latest edition is 2020, which incorporates the addenda issued since the release of the 2016 version. The standard goes through continuous maintenance by an ASHRAE standing standard project committee, so it’s regularly updated.
The purpose of the standard is to define data communication services and protocols for computer equipment used for monitoring and control of heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) and other building systems. It also works to define an abstract object-oriented representation of information communicated between such equipment, thereby facilitating the application and use of digital control technology in buildings. Therefore, the standard provides requirements for building control system communication protocols.
How is the ASHRAE 135 standard used?
The standard provides a set of communication protocols for transferring encoded data between devices. Examples of this data could be hardware, binary and analog input and output values, schedules, alarms and other event information. It could also be trend data, control logic, configuration information and other files and information. ASHRAE calls this standard control protocol building, automation and control networks (BACnet). The standard has its architecture rooted in the open system interconnection (OSI) basic reference model, ISO 7498, which is an international standard that defines a requirement for multiple protocol communication standards.
The standard was designed to meet the needs of building system communication protocol. The standard has these primary characteristics:
- Nearly all devices are peers, except some devices have higher level priorities for reading and writing the properties of objects and mutually acceptable execution of other services.
- The devices are all accessible and called objects. Each object has certain properties. Because of the ISO route, the standard has a layered approach to communication. This allows for future flexibility and opportunities for manufacturers to create new content and capabilities aligned with the protocol, thereby making it relevant in the future.

What is a control system?
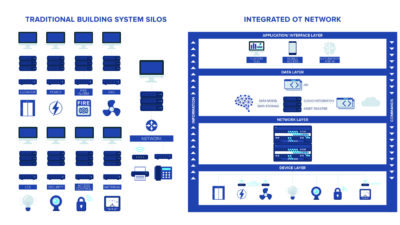
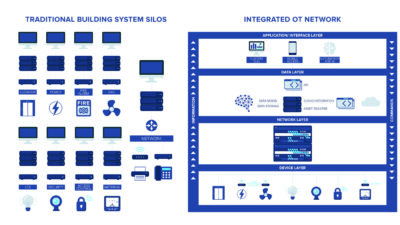
A control system is defined as a centralized method for operation of a building systems. This could include HVAC, lighting, shading, access control, security and other systems that may benefit in an interrelated environment. The objectives of a building automation control system are occupant comfort, efficient operation, reduction of energy consumption, reduce operating and maintenance costs and increased security of the automation system.
A control system is a defined method to transfer information from one building automation system device to another. BACnet allows for sending and receiving these electronic messages.
BACnet building automation systems
One capability of the building automation system (BAS) is that it can provide a comfortable environment. An example of this is with temperature control. It’s known in the HVAC industry that a comfortable temperature can be a very subjective value when talking to building occupants. The communication from a temperature sensor or thermostat, wired or wireless, can be used to send these commands. These devices allow users to adjust for different comfort levels or meet special requirements. The capability of communication allows for adjustment at individual locations throughout a building instead of a single location that will create a global command.
One of the uses of a BAS is data collection. This could be collecting all types of data having to do with various systems in a building. ASHRAE 135 establishes a layered approach for data exchange. BACnet does not require a rigid network layout rather it allows for devices to be connected through various means on local area networks. These connections could be direct physical links using master-slave/token passing (MS/TP) or through logic with BACnet internet protocol.
This layered approach is less complex than the standard that it’s rooted in — the OSI seven-layered system. BACnet uses a four-layered system with physical, data link, network and application layers. This data can be stored, analyzed and reported in various formats to help a user utilize the data to suit their needs.
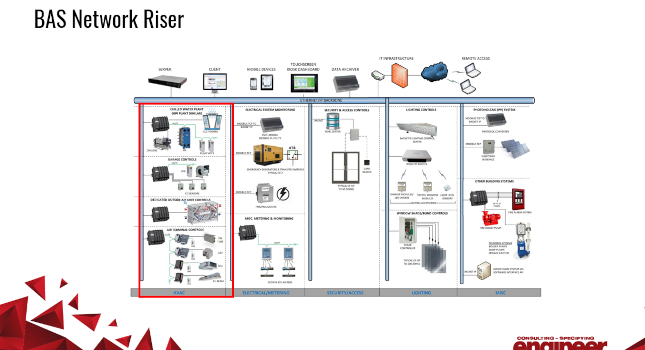
Figure 1 is an example of many systems that could be incorporated into a BAS network riser. The thick horizontal line across the top of this graphic shows the ethernet IP backbone. Connected directly to the backbone may be devices including servers, touchscreens, archive devices, mobile devices and IT infrastructure that allow remote access to the systems downstream.
The vertical lines represent the main trunk connections to the backbone. These are generally identified by different control system groups including HVAC, electrical systems, security, lighting and other miscellaneous systems such as photovoltaic fire sprinkler systems or plumbing equipment.
Common system protocols
There are three primary protocols. BACnet is configured as a client-server architecture. Modbus is a serial communication protocol developed by Modicon in the late 1970s. It was established as a method for transmitting information over serial lines between control devices. LONworks, created in the late 1980s, is a peer-to-peer system that can exchange data with any other LONworks device on the same network. It’s a distributed control system type. This system exchanges data directly between devices and can send a signal over a number of different wiring configurations including twisted pair ethernet or power lines.